How AI Engines Actually Work
The Hidden Algorithm: How ChatGPT Decides Which Websites to Cite
AI engines don't work like Google. They don't care about your domain authority or backlink count. Here's what they actually look for—and why it changes everything about content optimization.
From Keywords to Understanding
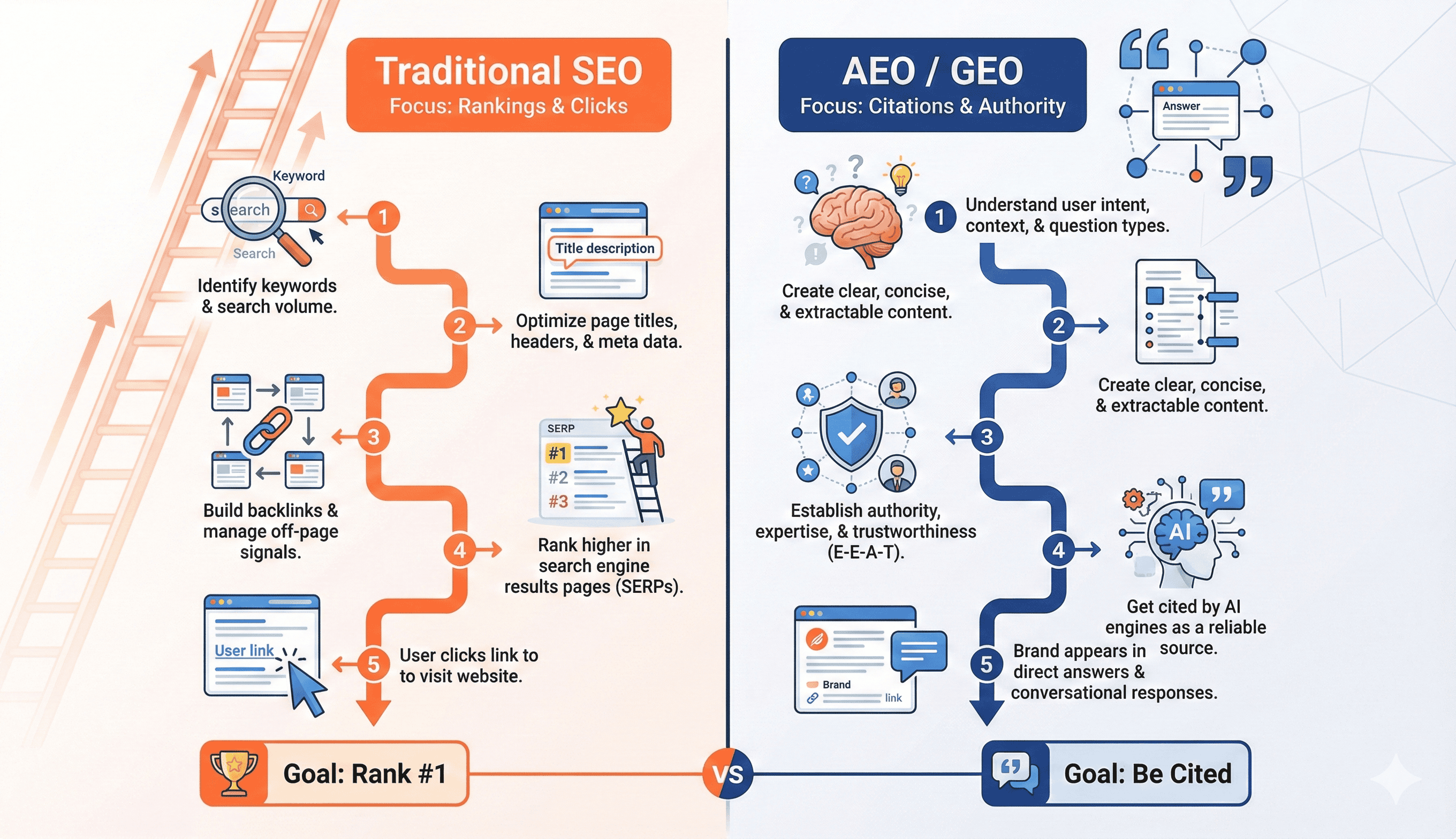
Traditional SEO and AEO operate on fundamentally different principles.
Traditional SEO: Keyword Matching
Google's algorithm primarily looks for:
- Keyword density and placement
- Backlink quantity and quality
- Domain authority and age
- Technical SEO factors (site speed, mobile-friendliness)
- User engagement signals (click-through rate, time on site)
The focus: Matching search terms to indexed pages and ranking them by authority signals.
AEO: Semantic Comprehension
AI engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Claude work differently. They:
- Read and comprehend your content like a human would
- Understand context and meaning, not just keywords
- Synthesize information from multiple sources
- Extract specific claims that answer the user's question
- Cite sources that provided clear, authoritative information
The focus: Understanding what you're actually saying and whether it reliably answers the user's question.
Why This Matters
Example: Running Shoes
Traditional search query: "best running shoes"
- Google matches keyword "running shoes"
- Returns pages with high backlink counts and keyword optimization
- User clicks through 3-5 sites to compare
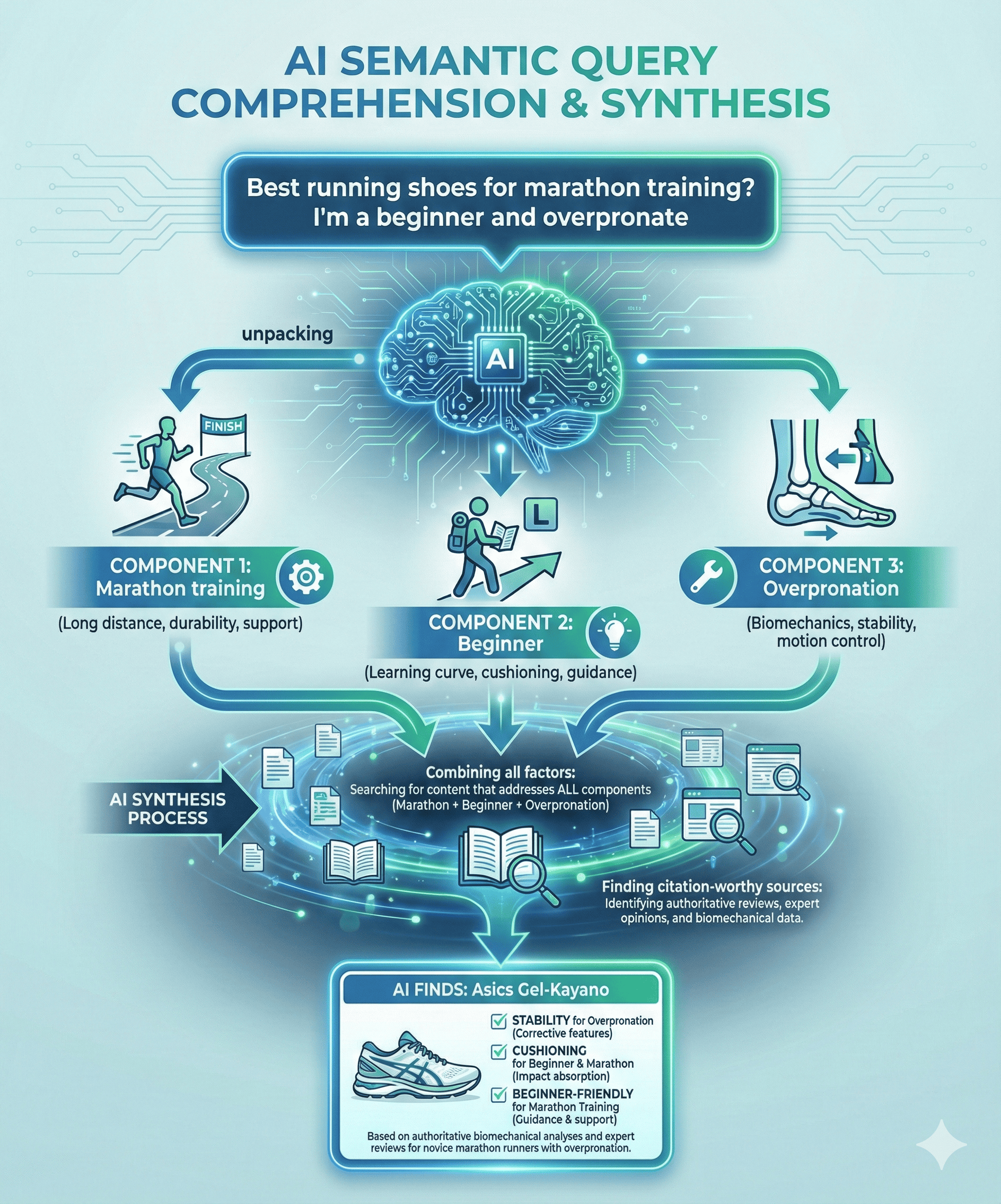
AI search query: "What are the best running shoes for someone training for their first marathon who has mild overpronation?"
- ChatGPT understands: beginner marathoner + biomechanical need + specific use case
- Searches multiple sources for comprehensive information
- Synthesizes an answer addressing training needs, overpronation support, and beginner considerations
- Cites 3-5 sources that provided the most relevant, clear information
The difference: AI understands nuance and context that keyword matching can't capture.
The Citation Decision Process
When an AI engine generates a response, here's what happens behind the scenes:
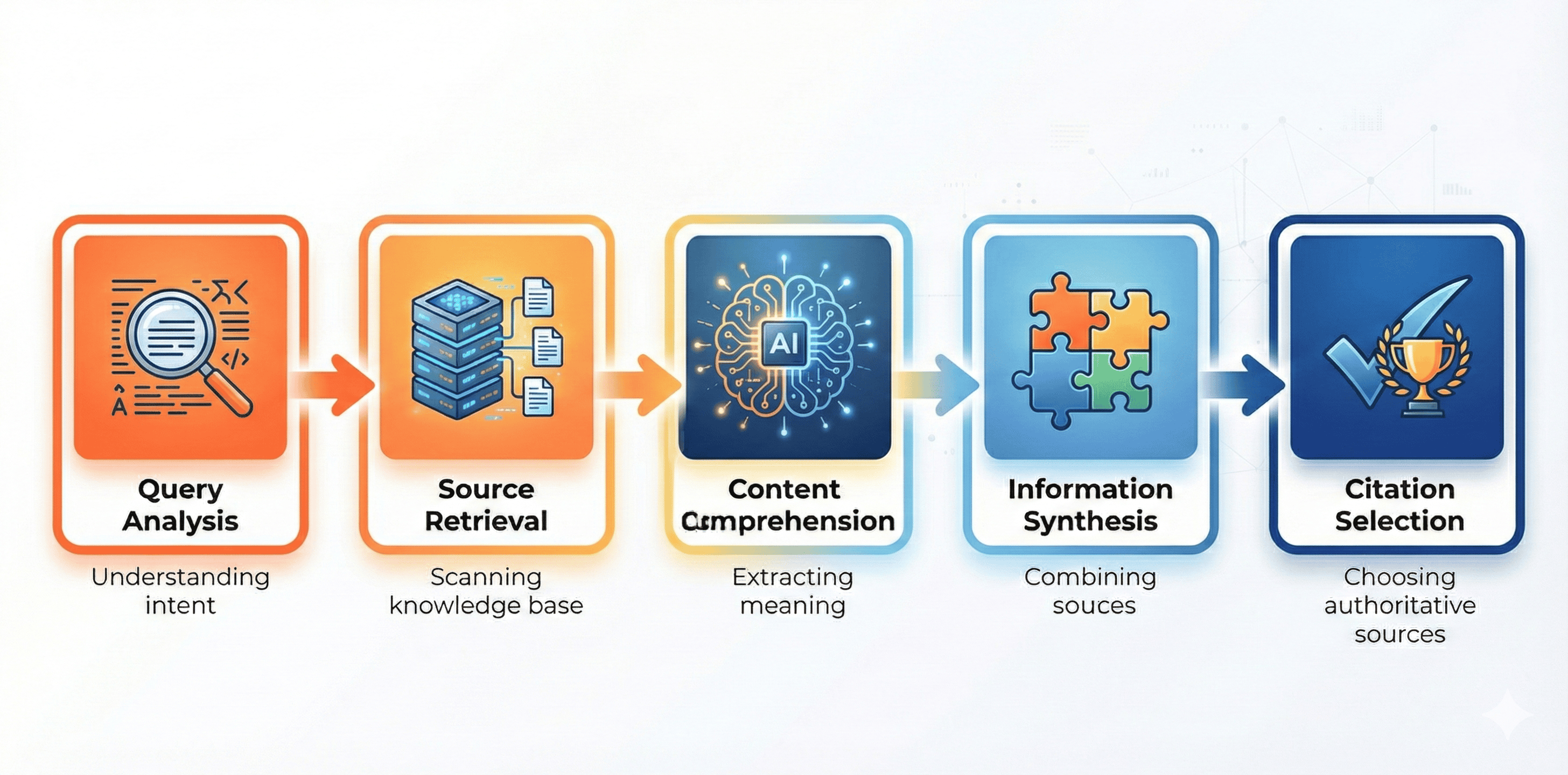
Step 1: Query Analysis
The AI breaks down the user's question to understand intent, context, and what type of answer is needed.
Step 2: Source Retrieval
The AI searches for relevant sources—similar to a traditional search engine, but with semantic understanding. It retrieves 5-20 potentially relevant sources.
Step 3: Content Comprehension
Here's where it gets different. The AI reads the full content of each source, understanding:
- What claims are being made
- How authoritative those claims are
- Whether information is backed by data
- How clearly ideas are expressed
- Whether statements are self-contained and extractable
Step 4: Information Synthesis
The AI combines information from multiple sources to create a comprehensive answer, prioritizing:
- Clear, specific statements
- Data-backed claims
- Authoritative sources
- Complete, extractable sentences
Step 5: Citation Selection
The AI cites sources that:
- Directly supported key points in the answer
- Provided unique or authoritative information
- Were clear and easy to extract from
- Contained verifiable claims
Critical insight: AI engines favor content that's easy to understand, extract, and verify. Vague, fluffy content gets ignored.
What Makes Content "Citation-Worthy"?
Based on the Princeton University study and real-world testing, here are the factors that increase your chances of being cited:
1. Clarity
Information must be easy to extract and understand.
❌ Poor Example
"Our innovative platform leverages cutting-edge technology to deliver transformative solutions that empower organizations to achieve their strategic objectives through digital transformation initiatives."
✓ Citation-Worthy
"Our platform reduced client operational costs by 34% in Q1 2025 (internal study, n=150 companies)."
Why it works: Specific claim, quantifiable result, source attribution, zero ambiguity.
2. Authority
Content demonstrates genuine expertise, not marketing fluff.
Signals of authority:
- Specific data and statistics
- Citations to reputable sources
- Expert quotes and perspectives
- Case studies with real numbers
- Research methodology transparency
❌ Vague
"We're experienced business attorneys."
✓ Citation-Worthy
"Our firm has closed 500+ M&A transactions totaling $2.3B since 2020."
3. Completeness
Statements are self-contained—they make sense without surrounding context.
Incomplete: "It's also very fast."
Complete: "The platform processes 10,000 transactions per second."
Why this matters: AI engines extract individual sentences. If a sentence requires the previous paragraph for context, it won't be cited.
4. Credibility
Claims are backed by verifiable data, sources, and examples.
❌ Without Credibility
"Our customers love our product."
✓ With Credibility
"4.8/5 average rating from 2,400+ verified customers (G2, 2025)."
Elements of credibility:
- Statistics with sources
- Third-party validation
- Specific numbers (not ranges)
- Dates and recency
- Methodology transparency
The Princeton Study: The Science Behind AEO
What the research found
In 2024, researchers at Princeton University conducted the first comprehensive study of how generative AI engines cite sources. Published in the ACM KDD conference, the study analyzed thousands of AI-generated responses.
Key findings:
91% of citations are under 18 tokens
AI engines overwhelmingly prefer short, complete sentences (approximately 12-15 words). Longer passages require summarization, which introduces errors and reduces citation confidence.
Optimization methods boost visibility by 40%
The study tested nine different optimization strategies. The most effective methods—adding citations, quotations, and statistics—increased visibility by 30-40%.
Keyword stuffing doesn't work
Traditional SEO tactics like keyword stuffing actually decreased visibility in AI responses. AI engines penalize content that appears manipulative.
Domain-specific strategies matter
The effectiveness of optimization methods varied significantly by industry. What works for SaaS companies differs from what works for professional services.
Source: Aggarwal, P., et al. (2024). "GEO: Generative Engine Optimization." ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining.
Real-World Examples by Industry
SaaS Company: Clear Feature Claims
Before AEO: "Our platform offers robust collaboration features."
After AEO: "Teams using our platform reduce meeting time by 40% (study of 200 companies, 2024)."
Result: Cited by ChatGPT in 15 of 20 relevant queries within 6 weeks.
Professional Services: Specific Expertise
Before AEO: "We help companies with digital transformation."
After AEO: "We've implemented AI automation for 85 Fortune 500 companies since 2022."
Result: Citation rate increased from 10% to 55% in industry-related queries.
E-commerce: Product Specifications
Before AEO: "High-quality outdoor gear for enthusiasts."
After AEO: "Our tents withstand 60mph winds and temperatures to -20°F (tested per ASTM F1934)."
Result: Now cited in technical product recommendation queries, 3.2x conversion rate.
Knowledge Check
Question 1: What's the main difference between how Google and ChatGPT evaluate content?
Answer: Google primarily uses keyword matching and link signals to rank pages. ChatGPT reads and comprehends content semantically, understanding meaning and context rather than just matching keywords. AI engines extract and synthesize information based on clarity, authority, and completeness—not backlinks.
Question 2: According to the Princeton study, what percentage of AI citations are under 18 tokens (approximately 12-15 words)?
Answer: 91%
The vast majority of AI citations are short, complete sentences under 18 tokens. This is because AI engines can extract these verbatim without risk of error or hallucination. Longer passages require summarization, which reduces citation confidence.
Question 3: Which of these is more citation-worthy?
A) "We're a leading provider of innovative solutions."
B) "We serve 2,400+ enterprise clients across 40 countries."
Answer: B
Option B is far more citation-worthy because it:
- Contains specific, verifiable numbers
- Is a complete, extractable statement
- Demonstrates scale and authority
- Avoids vague buzzwords ("leading," "innovative," "solutions")
Option A is generic marketing language that AI engines typically ignore.
Key Takeaways
- AI engines read and comprehend content semantically, not just match keywords
- The citation process has 5 steps: query analysis → source retrieval → content comprehension → synthesis → citation selection
- Citation-worthy content has 4 qualities: Clarity, Authority, Completeness, and Credibility
- 91% of citations are under 18 tokens (12-15 words)—short, complete sentences win
- Princeton research shows 40% visibility boost with proper optimization methods
What's Coming Tomorrow
Now you understand how AI engines select citations. Tomorrow, you'll learn the three specific content patterns that make AI engines 40% more likely to cite your website.
Day 3 Preview: The Power Patterns: 7-Word Phrases, 18-Token Rules, and Token Limits
Continue to Day 3 →Ready to Analyze Your Content?
Use Our Free Token Counter Tool
Paste any sentence from your website and instantly see if it meets the 18-token threshold that AI engines prefer.
Try the Token Counter →Sources Cited in This Lesson:
- Princeton University GEO Study (Aggarwal et al., 2024) - ACM SIGKDD Conference
- OpenAI ChatGPT Architecture Documentation, 2024
- Perplexity.ai Citation Methodology, 2024
- BrightEdge AI Search Performance Study, 2025
 5dayAEO
5dayAEO